Bay leaf
Category : Ayurvedic / Medicinal Plants
Description
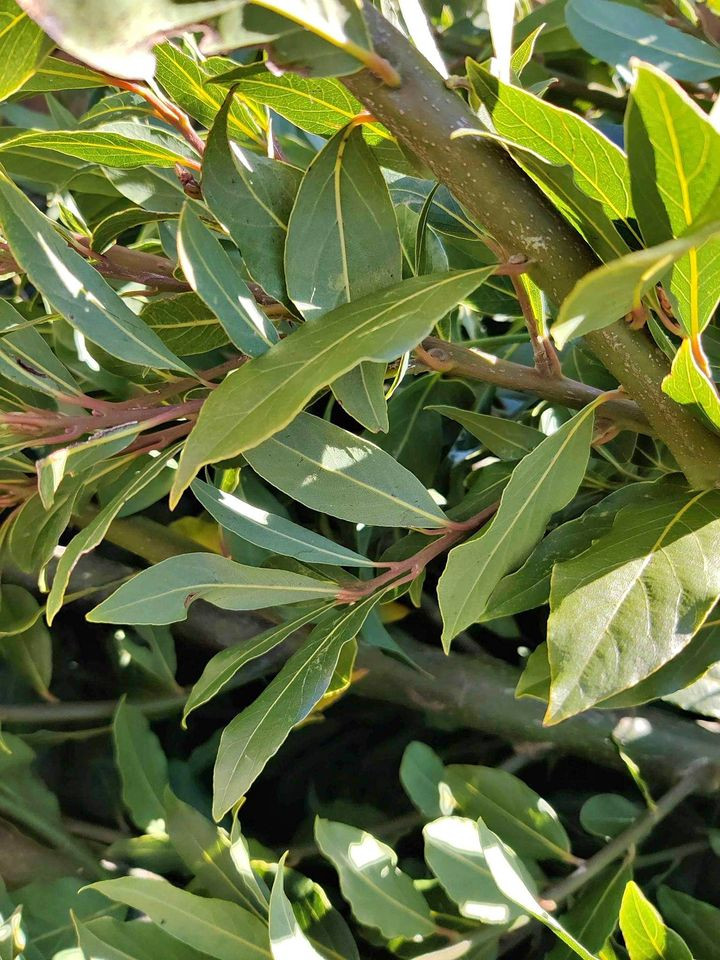
Bay leaf, also known as laurel leaf, is the leaf of the sweet bay tree, Laurus nobilis. This tree is an evergreen member of the Lauraceae family and is indigenous to countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea.
Botanical Characteristics
- Family: Lauraceae
- Genus: Laurus
- Species: L. nobilis
- Common Names: Bay leaf, laurel leaf, sweet bay, bay tree
Appearance
- Leaves: The leaves are oval, pointed, and smooth-edged, with a glossy dark green appearance on the upper side and a lighter green underside. They are typically 5-10 cm long and 2-4 cm wide.
- Tree: The bay tree is an evergreen that can grow up to 12-15 meters tall. It has a sturdy trunk and smooth bark.
Habitat
Bay trees are native to the Mediterranean region. They thrive in warm climates and are commonly found in countries such as Greece, Turkey, Italy, and Spain. They prefer well-drained soil and full sunlight but can tolerate partial shade.
Uses
Culinary Uses: Bay leaves are a popular spice in various cuisines. They are used to add flavor to:
- Stews
- Soups
- Sauces
- Marinades
- Pickling solutions
- Stuffings
- Fish dishes
The leaves are often added whole to dishes during cooking and removed before serving due to their bitter taste if consumed directly.
Medicinal Uses: In Ayurvedic and traditional medicine, bay leaves are valued for their therapeutic properties. They are used for:
- Digestive Health: Bay leaves can help stimulate the appetite, relieve indigestion, and reduce flatulence.
- Respiratory Health: They are used in remedies for coughs, colds, and respiratory infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Bay leaves contain compounds with anti-inflammatory effects, useful in treating conditions like arthritis.
- Antimicrobial Effects: The essential oils in bay leaves have antimicrobial properties that can help prevent infections.
Other Uses:
- Aromatherapy: The essential oil derived from bay leaves is used in aromatherapy for its calming and stress-relieving effects.
- Insect Repellent: Bay leaves can be used to repel insects such as moths and cockroaches.
Active Compounds
Bay leaves contain several bioactive compounds, including:
- Eucalyptol (Cineole): A major component of the essential oil, known for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
- Linalool: Contributes to the fragrance and has stress-reducing effects.
- Methyl Chavicol: Provides a distinctive aroma and has potential therapeutic benefits.
- Tannins: Contribute to the astringent properties of the leaves.
Safety and Precautions
While bay leaves are generally safe for culinary use, they should not be consumed whole due to their tough, fibrous texture which can be a choking hazard or cause damage to the digestive tract. It is important to remove the leaves from dishes before serving. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should use bay leaves with caution and consult a healthcare provider before using them medicinally.
Cultural Significance
Bay leaves have a rich history and cultural significance. In ancient Greece and Rome, they were symbols of honor and victory, often used to crown victors in athletic competitions and military commanders. The term "laureate," as in "poet laureate," derives from this tradition.
Conclusion
Bay leaves (Laurus nobilis) are a versatile and valuable plant with a wide range of uses in culinary, medicinal, and other applications. Their distinctive aroma and flavor make them a staple in many kitchens around the world, while their therapeutic properties are harnessed in traditional medicine.
Price : $25 $20
In Stock